THE SCIENCE
Unlike THC, which is intoxicating because it activates CB1 receptors in the brain, TYNA-1 is a CB1 blocker and a CB2 activator—both of which help in the treatment of addiction.
We believe that the pharmacokinetics data of TYNA-1 may support cessation after the first dose.
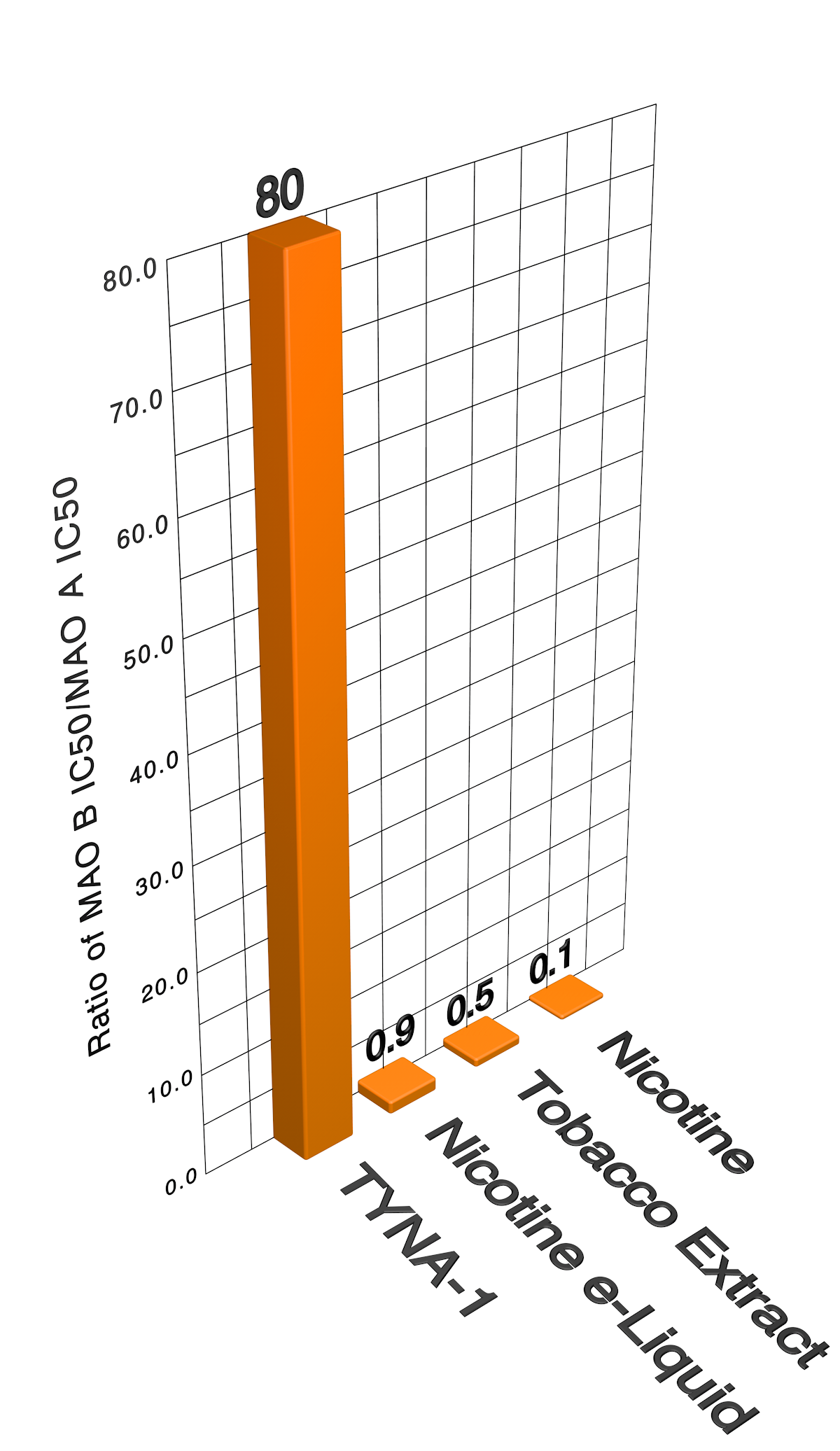
TYNA-1’s profile shows its inhibition of MAO B relative to MAO A is 80 fold greater than that of nicotine, demonstrating TYNA’s potent ability to block the reward signals from smoking while simultaneously preventing the withdrawal symptoms from smoking cessation.
Source: Eurofins Panlabs Discovery Services Taiwan, Ltd., and Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
An Unmet Need
The global tobacco market size was valued at USD 849.9 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.4% from 2022 to 2030. Cigarette smoking cost the United States more than $600 billion in 2018, including:
Healthcare spending related to smoking
Lost productivity due to illnesses and health conditions from smoking
Lost productivity due to premature death from smoking
Lost productivity due to premature death from secondhand smoke exposure
https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/cessation/smoking-cessation-fast-facts/index.html
Most Adult Smokers Want to Quit!
%
Smokers who said they want to quit (2015) (22.7 million)
%
Adult smokers who try and succeed in quitting each year
%
Adult smokers who successfully quit in 2018 (2.9 million)
https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/economics/econ_facts/index.htm
